
Side effects of steroids
Comprehensive Overview of the Side Effects of Steroids
Steroids are synthetic versions of hormones that occur naturally in the body. They are commonly used for their powerful anti-inflammatory effects and to treat various conditions, including asthma, arthritis, skin disorders, and autoimmune diseases. However, steroids can have significant side effects, especially with prolonged use or when used improperly. These side effects can vary depending on the type of steroid (oral, injectable, topical) and the dosage. This article will explore the side effects of steroids across various forms of administration and for different populations.
1. Side Effects of Steroids in General
Steroids are commonly classified into two main types:
- Corticosteroids: These are used to reduce inflammation and treat conditions such as asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, and skin conditions.
- Anabolic Steroids: These are synthetic substances similar to the male sex hormone testosterone and are often abused for muscle-building purposes.
While corticosteroids have widespread medical use, their long-term or improper use can lead to numerous side effects.
Common Side Effects of Steroids:
Weight Gain: Corticosteroids can increase appetite and alter fat distribution, often leading to weight gain.
Mood Changes: Steroids can cause irritability, anxiety, and mood swings. In some cases, they can lead to depression or even steroid-induced psychosis.
Insomnia: Steroids can disrupt sleep patterns, especially when taken in high doses or at night.
High Blood Pressure: Long-term use can cause fluid retention, increasing blood pressure.
Increased Blood Sugar: Steroids can impair insulin sensitivity, leading to higher blood sugar levels, which is a concern for people with or at risk of diabetes. Osteoporosis: Chronic use of steroids can interfere with bone health, leading to thinning of bones and increased fracture risk.
Weakened Immune System: Long-term steroid use suppresses the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections.
Cataracts and Glaucoma: Prolonged steroid use can increase the risk of eye conditions like cataracts (clouding of the lens) and glaucoma (increased pressure in the eye). 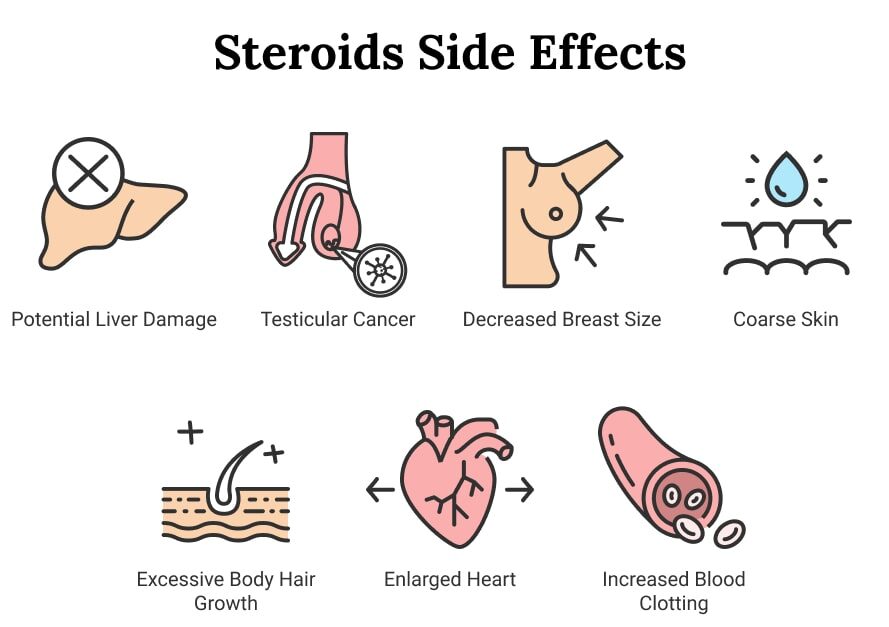
2.Side Effects of Steroid Tablets (Oral Steroids)
Steroid tablets, like prednisone or prednisolone, are often prescribed for conditions such as inflammatory diseases, autoimmune disorders, and allergies. Although effective, their systemic nature can lead to a range of side effects:
Short-term Side Effects:
Fluid Retention: Swelling of the ankles, feet, and face is common.
Elevated Blood Sugar: Can cause a temporary rise in blood sugar levels.
Indigestion and Stomach Ulcers: Steroids can irritate the stomach lining, leading to heartburn or ulcers.
Increased Appetite and Weight Gain: Steroids can cause significant changes in eating habits.
Acne and Skin Breakouts: The increased oil production in the skin may result in acne.
Long-term Side Effects:
Adrenal Suppression: Prolonged use can suppress the body’s ability to produce natural cortisol, leading to adrenal insufficiency when the steroid is discontinued.
Muscle Weakness: Chronic use can lead to muscle wasting and weakness.
Cushing’s Syndrome: This condition is caused by prolonged steroid use, leading to a characteristic “moon face,” fat deposits on the back of the neck, and thinning of the skin.
3.Side Effects of Steroid Injections
Steroid injections are often used to treat localized conditions, such as joint pain, tendonitis, and inflammation. The steroids are injected directly into the site of inflammation, providing rapid relief. However, this method can also come with side effects.
Common Side Effects:
Local Skin Reactions: Redness, swelling, or irritation at the injection site.
Joint Damage: Repeated steroid injections into the same joint may lead to cartilage damage and increased risk of joint deterioration.
Infection: Anytime there is an injection, there is a risk of infection at the injection site, especially if proper hygiene is not followed.
Nerve Damage: Rarely, steroid injections can damage nerves, leading to numbness or tingling in the area.
Systemic Effects: Although less common, repeated injections can lead to the systemic side effects seen with oral steroids, including weight gain, mood changes, and elevated blood sugar.
4.Side Effects of Steroids on Children
Steroids are sometimes prescribed to children for conditions such as asthma, eczema, or certain autoimmune diseases. However, children are particularly vulnerable to some of the side effects of steroids due to their developing bodies.
Common Side Effects in Children:
Growth Suppression: Long-term use of steroids can stunt growth in children, especially if taken in high doses over a long period.
Behavioural Changes: Steroids can affect mood and behavior, leading to irritability or aggression.
Bone Health: Like in adults, steroids can interfere with bone development, leading to an increased risk of fractures and osteoporosis.
Delayed Puberty: High doses of steroids can delay the onset of puberty in adolescents.
5.Side Effects of Steroids on Skin
Steroids can have several impacts on the skin, especially when used topically for conditions like eczema or psoriasis. Both systemic and topical steroids can cause various dermatological issues.
Systemic Steroid Side Effects on the Skin:
Thinning Skin: Prolonged use of oral or injected steroids can cause thinning of the skin, making it more fragile and prone to bruising and tearing.
Stretch Marks: Skin may become more elastic, leading to the formation of stretch marks, particularly on the abdomen, thighs, or arms.
Acne and Skin Breakouts: Steroid use can increase the production of oil in the skin, resulting in acne outbreaks.
Increased Risk of Infections: A weakened immune response from systemic steroid use can make the skin more susceptible to infections.
Topical Steroid Side Effects:
Skin Atrophy: Long-term use of topical steroids can lead to thinning of the skin, especially on sensitive areas like the face or genitals.
Steroid Rosacea: Chronic use of topical steroids on the face can lead to rosacea-like symptoms, including redness, pimples, and visible blood vessels.
Perioral Dermatitis: A condition that can occur with topical steroid use around the mouth, resulting in red bumps and irritation.
Hypopigmentation: Topical steroids can cause lighter patches of skin, particularly in darker-skinned individuals.
6.Side Effects of Steroids in Women
Steroids can affect women differently than men due to the hormonal differences between the sexes. Anabolic steroids can have significant side effects for women.
Common Side Effects in Women:
Menstrual Irregularities: Steroids can interfere with the menstrual cycle, causing irregular periods or amenorrhea (absence of menstruation).
Excessive Hair Growth: Anabolic steroids can cause hirsutism, or excessive hair growth, in areas like the face, chest, and back.
Deepening of the Voice: Prolonged use of anabolic steroids can cause voice deepening due to changes in the vocal cords.
Clitoral Enlargement: Long-term use of anabolic steroids may lead to a permanent enlargement of the clitoris.
Breast Shrinkage: Some women who use anabolic steroids may experience a reduction in breast tissue size.
7.Side Effects of Steroid Creams (Topical Steroids)
Steroid creams are often prescribed for dermatological conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and allergic skin reactions. While these creams are typically safe when used short-term, prolonged or excessive use can cause side effects.
Side Effects of Topical Steroids:
Skin Thinning: Prolonged use of steroid creams can thin the skin, leading to increased fragility and bruising.
Striae (Stretch Marks): The skin may develop stretch marks in areas where the cream is applied frequently.
Contact Dermatitis: Ironically, some people may develop a contact allergy to the steroid cream itself, leading to a red, itchy rash.
Rosacea: Chronic use of topical steroids on the face can result in rosacea-like symptoms, including redness and pimple-like bumps.
Hypopigmentation: Steroid creams may cause lighter patches of skin, particularly in people with darker skin tones.
Perioral Dermatitis: This condition, characterized by a rash around the mouth, can be exacerbated by topical steroid use.
Conclusion
Steroids, whether taken orally, injected, or applied topically, are powerful medications with significant therapeutic benefits. However, their side effects should not be overlooked, especially with long-term use or misuse. Understanding the potential side effects can help patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions about steroid use, balancing the benefits with the risks. For individuals who require steroids, it is important to use them under medical supervision and to follow prescribed dosages and treatment regimens to minimize the risk of adverse effects.